AI Explained for Beginners: Prompt, Agent, MCP & Function Calling
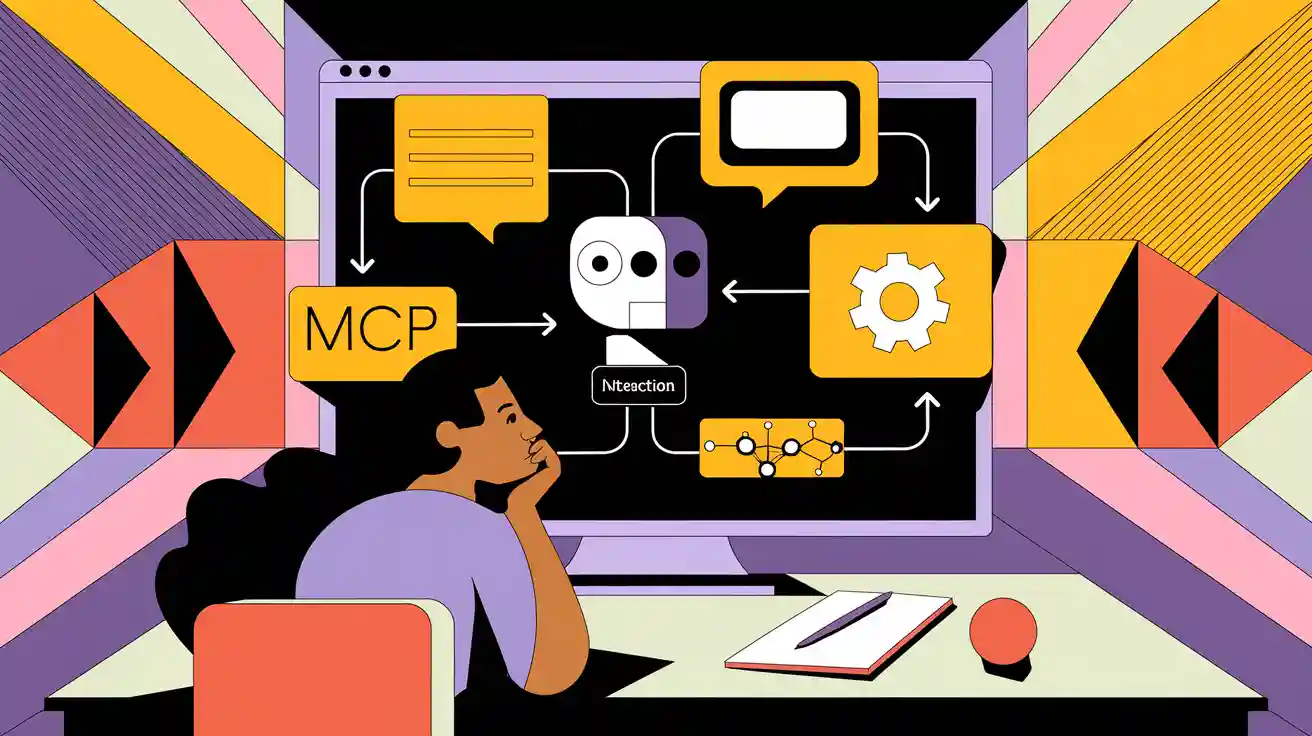
You might ask what a prompt, agent, MCP, and function calling mean in AI Explained. A prompt is like instructions you give to a digital helper. An agent is a smart helper that follows prompts and uses functions to do jobs. MCP, or Model Context Protocol, lets agents connect to tools and data. This makes things work well and keeps them safe. With function calling, the AI can use special functions. It is like using different apps on your phone. Knowing these basics helps you use AI tools better and safer. Recent studies show clear rules make AI more reliable, open, and trusted.
Key Takeaways
A prompt is a simple instruction you give to AI. It helps guide what the AI does and helps you get better answers.
AI agents are smart helpers. They read your prompt, make a plan, and use functions to finish tasks.
MCP (Model Context Protocol) links AI agents to many tools and data sources. It does this in a safe and easy way.
Function calling lets AI use other tools and apps. This helps AI get real-world information and do actions.
When you use prompts, agents, MCP, and function calling together, you get a strong AI workflow. This makes AI smart, flexible, and useful.
AI Explained
Key Concepts
When you explore ai explained, you find four main ideas: prompt, agents, MCP, and function. Each plays a special role in how modern llms work. A prompt is the instruction you give to an AI. It helps the system understand your user intent. Agents act as smart helpers. They use prompts to figure out what you want and then choose the right function to get the job done. MCP, or Model Context Protocol, is like a universal translator. It lets agents connect with tools, data, and even other prompts. This makes ai explained easier for everyone.
You can think of a function as a tool or action the AI can use. For example, if you ask an AI to check the weather, the agent uses a function to get that information. In ai explained, llms use prompts to guide their actions. They rely on agents to handle tasks and use MCP to access many functions. This setup helps llms understand your intent and respond in useful ways. Generative ai, powered by large language models, depends on these building blocks to work smoothly.
How They Connect
In ai explained, these concepts work together like a team. You start with a prompt that shows your intent. The agent reads your prompt and figures out what you want. It then picks the right function to use. MCP steps in to help the agent find and use the right tools or data. This process lets llms handle complex tasks, from answering questions to running apps.
Note: MCP makes it easier for agents to connect with many tools at once. This means llms can do more without extra work from you.
When you use ai explained tools, you see how prompts, agents, MCP, and function calling all support each other. They help llms understand user intent, choose the right function, and deliver helpful results. This teamwork makes modern AI systems powerful and easy to use.
Prompt
What Is a Prompt
A prompt is the instruction you give to an AI system. You use a prompt to tell the AI what you want it to do. Think of a prompt as a message you send to a smart helper. The AI reads your prompt and tries to understand your request. When you write a prompt, you guide the AI to use the right function for your task. The quality of your prompt affects how well the AI performs the function you need.
You can use different types of prompts. Some prompts give clear instructions, while others provide examples. A prompt can ask the AI to explain, summarize, or create something new. You might use a prompt to tell the AI to use a specific function, like checking the weather or writing a story. The structure and wording of your prompt matter. If you use a detailed prompt, the AI can choose the best function to answer you. Even small changes in your prompt can change the function the AI uses and the result you get.
Tip: Try using lists or step-by-step prompts. This helps the AI pick the right function and gives you better answers.
Prompt Examples
You can use many prompt styles to get the function you want. Here are some common prompt types and how they work:
Prompt Type | Description |
|---|---|
Zero-Shot Learning | You give a task with no examples. The AI uses your prompt to guess the function you want. |
One-Shot Learning | You give one example in your prompt. The AI learns which function to use from your example. |
Few-Shot Learning | You give a few examples. The AI finds the right function by looking at your prompt examples. |
Chain-of-Thought Prompting | You ask the AI to show its steps. The prompt helps the AI use a function for each step. |
Iterative Prompting | You build on your last prompt. The AI uses the function again with new details. |
Negative Prompting | You tell the AI what not to do. The prompt stops the AI from using the wrong function. |
Hybrid Prompting | You mix prompt types. The AI uses more than one function to solve your task. |
Prompt Chaining | You link prompts together. The AI uses a function for each prompt in the chain. |
Here are some real-world prompt examples:
You ask a chatbot to make a schedule. Your prompt tells the AI to use the calendar function.
You want a summary of a long article. Your prompt guides the AI to use the summarizing function.
You need a code snippet. Your prompt asks the AI to use the code generation function.
You want an image. Your prompt describes the scene, and the AI uses the image creation function.
You ask for a list of tips. Your prompt helps the AI use the list-making function.
The way you write your prompt helps the AI pick the right function. If you want better results, try changing your prompt and see how the function output changes. Many people use prompt engineering to get the best function from the AI. You can try different prompt types to see which function works best for your needs.
Autonomous AI Agents

Agent Basics
You use autonomous ai agents all the time, even if you do not notice. These agents are smart helpers that make choices and finish jobs for you. They use a function to figure out what you need. Then they pick the right function to fix your problem. You might see them in chatbots, smart home gadgets, or online help.
Autonomous ai assistants have some key traits:
They work by themselves and do not need much help from people.
They change and learn when things are different.
They use many kinds of data, like words, pictures, or sounds, to decide better.
They remember what they did before and use that to get better.
They make plans and follow steps to finish jobs.
They use a function to connect with tools, apps, or the web.
They learn from feedback and improve over time.
They look at outside sources, like websites or APIs, to find answers.
You can think of an agent as a digital worker. It uses a function to sense what you want. Then it thinks about the best way to help and acts to get results. This is called autonomous decision making. The agent does not just wait for you to tell it what to do. It can set goals, plan steps, and use a function to reach those goals.
Agent Roles
Agents do many jobs in real life and business. You find them in customer support, healthcare, money, and even schools. Each agent uses a function to do tasks in its area. For example, a customer support agent uses a function to answer questions, fix problems, and send issues to others if needed. In healthcare, agents use a function to handle patient records, set up visits, and check supplies.
Here are some common agent jobs:
Role | What the Agent Does |
|---|---|
Virtual HR Agent | Uses a function to answer worker questions and manage benefits. |
Finance Agent | Uses a function to spot odd spending, update plans, and track costs. |
Healthcare Agent | Uses a function to check staff, set schedules, and manage supplies. |
Education Agent | Uses a function to help students, plan classes, and track grants. |
Retail Agent | Uses a function to set schedules, watch stock, and help shoppers. |
You also see different kinds of agents. Reactive agents use a function to answer simple requests. Proactive agents use a function to guess what you need and act before you ask. Conversational agents use a function to talk with you and remember your questions. Each type uses a function in its own way to give you the answer you need.
When you use an AI tool, the agent works in the background. It uses a function to get information, make choices, and give you the answer. This teamwork between agents and function makes things easy and helpful for you.
Function Calling
How Function Calling Works
Function calling lets you connect AI models to tools, apps, and data outside the AI itself. When you give an AI a prompt, it can decide if it needs to use a function to help you. The process works in clear steps:
You send a prompt that may need outside help.
The AI checks if it needs to use function calling.
If needed, the AI picks the right function from a list of available functions.
The AI will generate function arguments, which are details the function needs.
The system will execute function by sending these arguments to the function.
The function runs and sends back results.
The AI uses the results to answer your question or finish your task.
You can think of function calling as the AI making a phone call to another app or tool. The AI knows which functions to use because developers define them, often using user defined functions with clear names and rules. The AI can even handle more than one function in a conversation, keeping track of each step.
Function calling helps AI do things like check the weather, look up facts, or control smart devices. It bridges the gap between what the AI knows and what it can do in the real world.
Real-World Uses
You see function calling in many places every day. AI assistants use function calling to fetch your recent orders or track a package. When you ask to schedule a meeting, the AI uses function calling to check your calendar and find a good time. In online shopping, function calling helps the AI search for products or show you details about an item.
Function calling lets AI:
Solve math problems by using special functions.
Build workflows that turn messy data into neat lists.
Update maps or apps by calling functions that change what you see.
Give real-time answers by connecting to live databases.
Generate function arguments for each task, so the right function gets the right info.
Customer support bots use function calling to answer questions about your orders. In e-commerce, function calling helps with product recommendations and order tracking. You benefit from function calling because it makes AI smarter and more helpful. When you use an AI tool, function calling works in the background to execute function after function, making your experience smooth and fast.
MCP in AI
What Is MCP
You might wonder how AI links to many tools and data. MCP, or Model Context Protocol, is the way it happens. MCP is an open set of rules that lets AI connect to outside data, tools, and memory. Think of MCP as a bridge that works for everything. It helps AI agents use any function or tool without making new code each time.
Here is a table to help you see what MCP does:
Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
Definition | MCP is an open set of rules that lets AI systems safely connect both ways to outside data. It helps different tools work together and adds helpful tags to data. |
Technical Specifications | It has official rules, software kits, uses JSON-RPC 2.0 to send messages, and borrows ideas from the Language Server Protocol. |
Components | MCP servers share data, MCP clients are AI apps that connect to servers, Claude Desktop has local server support, and there are free server versions. |
Purpose | It replaces many different connectors with one set of rules. This makes it easier for AI tools to work together and use many tools at once. |
Adoption | Big AI groups and platforms use MCP. It is built into coding tools, research apps, and web building programs. |
Supported Languages & SDKs | You can use MCP with Python, TypeScript, C#, and Java. |
Use Cases | AI2SQL lets you ask databases questions, search research papers, get help coding, and make web content with AI. |
MCP lets you link AI helpers to content stores, work tools, and coding spaces. You can use MCP to break up data walls and make AI stronger. MCP keeps your data safe with two-way links, so AI can use each function without risk.
MCP and Tools
MCP changes how you use tools with AI. You do not need to make new code for every tool. MCP uses a client-server system. The MCP client is inside the AI app. The MCP server links to outside tools or data. When you give a prompt, the AI agent uses MCP to find out which function or tool it can use.
Here is how MCP works with tools and functions:
1. The MCP host, like a chat app, asks MCP servers for tools. 2. MCP servers answer with a list of things, like a weather API or a database function. 3. The host sends your question and the tool list to the AI model. 4. The AI model picks the best function to answer you. 5. The MCP client tells the MCP server to run the function or get data. 6. The MCP server runs the function and sends back the results. 7. The AI agent uses the results to finish your task.
You can use MCP to look up facts, run a function, or link to work systems. MCP lets AI agents find tools while they work, so you get easy access. Each function uses a standard JSON request and answer style. This helps AI search, call a function, and use the results.
MCP lets the AI use more than one function at once. You can search many places, run many functions, and get answers faster. MCP also keeps your data safe with built-in rules and checks. You can trust MCP to help AI search, use each function, and link to any tool you need.
AI Workflow
Putting It Together
You can see how prompt, agent, MCP, and function calling work together in a real AI workflow. Each part has a job, but they form a team when you use them in order. Here is how you can build a typical AI workflow:
You start by creating a prompt. You use an agent builder to help you write and refine your prompt. This guides the large language model (LLM) to understand your goal.
You break down big tasks into smaller steps. You use prompt chaining and structured outputs. This helps the agent handle complex jobs.
You connect to MCP servers. These servers let your agent reach outside tools, APIs, and services. You do not need to write new code for every tool.
You add function calling tools. You define tool schemas and set up mock responses. This step lets your agent know which function to use for each task.
You run your agent with function calling turned on. The agent can now call any function it needs, like checking the weather or running a search.
You test and improve your prompts and tool setups. You keep changing things until your agent works better.
You use the agent builder to generate code snippets. You can add these to your own apps or websites.
When you use this workflow, you give your AI the power to plan, search, and act. The agent can decide which function to use at each step. MCP makes it easy to find and use new tools. You do not have to worry about connecting every tool by hand.
Here is a simple table to show how each part fits into the workflow:
Step | What Happens |
|---|---|
Prompt | You tell the agent what you want. |
Agent | The agent reads your prompt and plans the steps. |
MCP | The agent uses MCP to find tools and data. |
Function Calling | The agent calls the right function, like a search or a calculator. |
Results | The agent uses the function output to answer you or finish the task. |
You can see this process in action when you ask an AI to search for news, summarize articles, or book a meeting. The agent reads your prompt, plans the steps, uses MCP to find the right tool, and calls the function. The function might run a search, check a calendar, or pull data from a database. The agent then uses the function result to give you a clear answer.
MCP helps by making every tool easy to find and use. You do not need to worry about which vendor made the tool. The agent can search for the best function and use it right away. This makes your AI workflow smooth and powerful.
Real-Life AI
You use AI workflows like this every day, even if you do not notice. Many companies use these building blocks to solve real problems. For example, OpenAI uses MCP in their agent SDK. This lets their agents call any function, search many sources, and work with different tools. They plan to expand MCP to cover more knowledge sources, like project management and data analytics.
Startups like Cynepia use agent builders with MCP. This helps them create smart apps that can search, plan, and act. These apps use function calling to connect with outside services. You see this in SaaS platforms, developer tools, and enterprise chatbots. The agent can search a database, call a function to update records, or pull information from a CRM.
Real-world AI systems use MCP to keep things safe and simple. MCP separates the model logic from the environment. This means your agent can search for tools, call any function, and keep track of what it does. You do not need to build custom connectors for every new tool.
Here are some ways companies use these workflows:
A code assistant can search project files, call a function to check code quality, and suggest fixes.
An enterprise chatbot can search a knowledge base, call a function to update a ticket, and send you a summary.
A desktop AI agent can search your files, call a function to open an app, and manage your schedule.
A natural language to SQL tool can search a database, call a function to run a query, and show you the results.
Multi-tool agents can search for answers, call many functions, and chain results together in one conversation.
You get many benefits from using a standardized workflow. MCP makes every function easy to find and use. You can search across platforms, scale your AI, and keep your data safe. Companies save time and money because they do not need to build new connectors for every tool. Security improves because MCP tracks every function call and search. You get audit logs and better control over who can use each function.
You should know that building these workflows can be hard. You may face problems with data quality, system complexity, and security. Sometimes, a function may not work as expected, or a search may return the wrong result. You need to watch for prompt injection, supply chain risks, and version changes. Good practices like modular design, audit logs, and human checks help keep your workflow safe.
When you use AI in your daily life, you rely on these workflows. You ask a question, the agent plans the steps, uses MCP to find tools, and calls the right function. The agent can search for answers, use the function output, and give you a clear response. This teamwork makes AI smart, safe, and helpful.
You have learned about prompts, agents, MCP, and function calling. These ideas show how AI tools work and make them easier to understand.
Aspect | Function Calling | MCP (Model Context Protocol) |
|---|---|---|
Purpose | Changes what you type into function steps | Finds and handles tools for the agent |
Flexibility | Only uses certain functions | Can use new tools without more coding |
Try out easy AI chatbots or no-code tools. Keep trying new things and learning. AI will keep changing, and you can get better too! 🚀
FAQ
What is a prompt in AI?
A prompt is the instruction you give to an AI system. You use prompts to tell the AI what you want. Clear prompts help the AI choose the right action or function.
How do AI agents help you?
AI agents act as smart helpers. They read your prompt, plan steps, and use tools or functions to finish tasks. You see agents in chatbots, smart devices, and online assistants.
What does function calling mean?
Function calling lets AI use outside tools or apps. When you ask for product details, the AI can call a function to find and show you the right information.
Why is MCP important in AI?
MCP connects AI agents to many tools and data sources. It uses open rules so agents can find and use new tools easily. MCP keeps your data safe and makes AI more flexible.
Can you use mistral models with these AI tools?
Yes, you can use mistral models with agents, MCP, and function calling. These models help AI understand prompts and work with many tools for better results.
See Also
A Simple Introduction To AI Agents For Beginners
Steps To Create And Deploy A Powerful LLM Agent
Complete Guide To Developing An AI Chatbot Using RAG

