Web Apps vs Websites Explained for Beginners in 2025: Differences, Tools, and More

A website is a collection of pages that delivers information to users, such as news, blogs, or company details. In contrast, a web app is an interactive platform that allows users to perform specific tasks, like shopping or editing documents.
The main difference lies in their purpose. Websites focus on sharing information, while web apps prioritize functionality and user interaction. Your choice between the two should depend on your goals and the kind of experience you want to provide.
What Is a Website?
Definition of a Website
A website is a collection of related web pages and multimedia content that share a common domain name. These pages are hosted on web servers and are accessible via the internet. Websites serve various purposes, including personal, corporate, governmental, or organizational goals.
Definition of a Website | Notable Examples | Purpose/Function |
|---|---|---|
A collection of related web resources including web pages and multimedia content, identified with a common domain name and published on at least one web server. | Wikipedia.org, Google.com, Amazon.com | Personal, corporate, government, or organization websites dedicated to specific topics or purposes. |
Characteristics of Websites
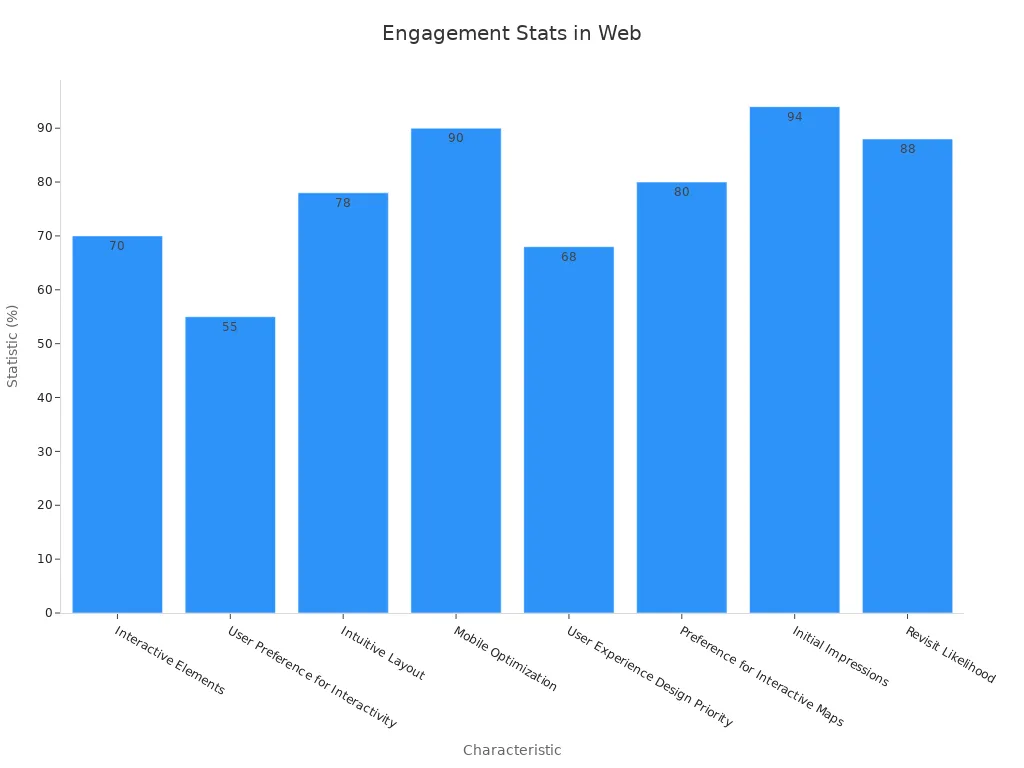
Websites are designed to deliver information and create a seamless user experience. They often include features like intuitive layouts, mobile optimization, and interactive elements that enhance engagement.
Characteristic | Statistic | Description |
|---|---|---|
Interactive Elements | Influence purchasing decisions among online shoppers. | |
User Preference for Interactivity | 55% | Prefer websites with interactive features over static ones. |
Intuitive Layout | 78% | Likelihood of users returning to a website with an intuitive layout. |
Mobile Optimization | 90% | Users believe interactive elements should be optimized for mobile devices. |
User Experience Design Priority | 68% | Web designers consider user experience design a top priority in 2023. |
Preference for Interactive Maps | 80% | Users prefer interactive maps over static ones for location-based information. |
Initial Impressions | 94% | Percentage of initial impressions formed by visitors to a website. |
Revisit Likelihood | 88% | Online consumers unlikely to revisit a website without engaging features. |
Common Use Cases for Websites
Websites are versatile and cater to a wide range of industries and purposes. Here are some common use cases:
Personal Blogs
Personal blogs allow individuals to share their thoughts, experiences, and expertise with a global audience. These websites often feature storytelling, tutorials, or niche topics that resonate with readers.
Business Websites
Business websites showcase products, services, and company information. They act as a digital storefront, helping businesses reach potential customers and establish credibility.
News Portals
News portals deliver real-time updates on current events, politics, entertainment, and more. These websites prioritize accessibility and mobile optimization to ensure users stay informed wherever they are.
Organizations across industries use websites to integrate real-time data, enhance decision-making with AI and machine learning, and adopt self-service tools for better data access.
Real estate
Travel
Jobs
Market research
What Is a Web App?
Definition of a Web App
A web app is a software application that runs on a web server and is accessed through a web browser. Unlike traditional desktop applications, web apps do not require installation. They combine the functionality of software with the accessibility of websites, offering users an interactive experience. Over the years, web development has evolved significantly, and by 2025, web apps are expected to leverage technologies like AI and Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) to deliver even more advanced features.
AI-powered web applications are becoming increasingly common, automating tasks and personalizing user experiences.
Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) are gaining traction, offering app-like functionality directly through browsers without requiring downloads.
Characteristics of Web Applications
Web applications stand out due to their unique features, which make them versatile and user-friendly. These characteristics include:
Interactivity: Web apps often include dynamic elements that allow users to engage with the platform actively. For example, filling out forms, uploading files, or editing documents directly within the app.
Platform Independence: You can access web apps on any device with a browser, whether it's a smartphone, tablet, or desktop. This flexibility eliminates the need for device-specific installations.
Real-Time Updates: Web apps can update content instantly without requiring users to refresh the page. This feature enhances user engagement and ensures a seamless experience.
Scalability: Businesses can easily scale web apps to accommodate growing user bases, making them ideal for companies of all sizes.
User engagement trends highlight the importance of these features. High engagement often indicates user satisfaction and retention. Metrics like daily active users, user stickiness, and retention rates are critical for measuring a web app's success. Strategies such as gamification and loyalty programs further enhance engagement.
Common Use Cases for Web Apps
E-commerce Platforms
E-commerce platforms like Amazon and Shopify are prime examples of web apps. They allow users to browse products, add items to their cart, and complete purchases—all within an interactive interface. Dynamic pricing, powered by real-time data collection, helps businesses adjust prices instantly to maximize profits.
Online Tools (e.g., Google Docs)
Online tools such as Google Docs and Canva enable users to create, edit, and share documents or designs in real time. These tools rely on cloud-based technology to provide a seamless and collaborative experience. By 2025, advancements in AI and machine learning are expected to make these tools even smarter, automating repetitive tasks and enhancing productivity.
Social Media Applications
Social media platforms like Facebook and Instagram are web apps that connect millions of users worldwide. They offer features like real-time messaging, content sharing, and personalized feeds. These platforms also utilize customer sentiment management to gather feedback and maintain brand reputation effectively.
Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
Dynamic Pricing | Automates real-time data collection from competitors to adjust prices instantly, enhancing profit margins. |
Enhanced Lead Generation | Identifies potential leads and analyzes customer sentiment through automated data collection. |
Customer Sentiment Management | Gathers customer feedback from various platforms to manage brand reputation effectively. |
Web apps continue to evolve, with trends like serverless architecture and low-code platforms simplifying development. These innovations make it easier for businesses to create powerful, scalable applications that meet diverse user needs.
Website vs Web App: Key Differences

Interactivity and Functionality
When comparing a website vs web app, interactivity and functionality are among the most noticeable differences. Websites primarily serve as static platforms that deliver information. For example, a news website allows you to read articles but doesn’t let you interact with the content beyond basic actions like clicking links. In contrast, a web application is designed to be interactive. It enables you to perform tasks such as filling out forms, uploading files, or even editing documents directly within the platform.
Web applications also require more complex backend services to process data and provide dynamic features. For instance, an e-commerce web app allows you to browse products, add items to your cart, and complete purchases—all actions that involve real-time data processing. Websites, on the other hand, are simpler to build and maintain because they consist of static pages with minimal interactivity.
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Measures how well user expectations are met through interactivity and functionality. | |
Time to Interactive | Indicates how quickly a platform becomes fully usable for user actions. |
Speed Index | Assesses how fast visible content is displayed to the user. |
Authentication and User Accounts
Authentication is another key difference between websites and web applications. Most websites allow public access without requiring you to log in. For example, you can visit a news website like The Guardian and read articles without creating an account. However, web applications often require user authentication to provide personalized services. Platforms like Google Docs or social media apps ask you to sign in before you can access their features.
This requirement for authentication ensures that web applications can store and manage user data securely. It also enables features like saving progress, customizing user experiences, and maintaining privacy. Websites, by contrast, are generally designed for broader public access and do not store user-specific data.
Type | Authentication Requirement | Examples |
|---|---|---|
Websites | The Guardian, The New York Times | |
Web Applications | Required | Google Docs, Facebook |
Scalability and Performance
Scalability and performance are critical factors when deciding between a website and a web application. A scalable website can handle increased traffic by optimizing resources during peak times. For example, a news website might experience a surge in visitors during breaking news events. By contrast, web applications must scale not only to accommodate more users but also to maintain seamless functionality for tasks like real-time collaboration or data processing.
Performance metrics such as response time and throughput highlight these differences. Websites typically focus on fast loading times and simple navigation. Web applications, however, prioritize features like real-time updates and error-free interactions. To ensure scalability, you should identify your platform’s needs, choose the right scaling approach (e.g., scaling up or out), and conduct load testing to address potential bottlenecks.
Metric | Description |
|---|---|
Response time | The time it takes for the system to react to a given input. |
Throughput | The number of transactions the system can process in a given time. |
System availability | The percentage of time the system is operational compared to total time. |
Resource utilization | The percentage of time a system resource is occupied compared to total time. |
By understanding these key differences, you can make an informed decision about whether a website or a web application is the right choice for your needs.
Development Complexity and Cost
When deciding between a website and a web app, understanding the development complexity and cost is crucial. Websites are generally simpler and more cost-effective to build. They often rely on pre-designed templates and straightforward coding, making them accessible even to those with limited technical expertise. In contrast, creating a web application involves a higher level of complexity due to its interactive features and dynamic functionalities.
The cost of developing a web application can vary significantly based on its complexity. Here’s a breakdown of typical expenses:
Research Phase: $1,000 – $15,000
Design Phase: $5,000 – $25,000
Development Phase: $20,000 – $100,000
Testing Phase: $5,000 – $20,000
Maintenance: $10,000 to $50,000 annually
Web applications often require a team of skilled developers, designers, and testers to ensure they meet user expectations. Complex applications, such as those supporting broad and unstructured goals, demand significant technical expertise. Additionally, the design and user experience (UI/UX) play a pivotal role in determining the overall cost and complexity. A well-designed interface not only enhances usability but also ensures the application aligns with user needs.
On the other hand, websites are more straightforward to develop. Platforms like WordPress and Wix offer drag-and-drop tools, reducing the need for extensive coding. This simplicity translates to lower costs, making websites an ideal choice for individuals or small businesses with limited budgets.
Maintenance and Updates
Maintaining and updating your platform is essential for ensuring its reliability and security. Websites typically require less maintenance compared to web applications. Automated scripts handle many functions, such as SEO updates and content management. However, technical glitches can still occur, leading to issues like downtime. Regular updates are necessary to patch vulnerabilities and keep the website running smoothly.
Web applications, on the other hand, demand ongoing maintenance to remain functional and secure. This includes tasks like upgrading software, correcting faults, and adapting to new requirements. For example, adding new features or improving performance often involves significant effort and resources. Neglecting maintenance can expose users to risks, such as data breaches or operational inefficiencies.
Here are some key aspects of maintenance for both platforms:
Websites:
Automated updates for SEO and content.
Security patches to address vulnerabilities.
Minimal downtime if managed properly.
Web Applications:
Regular updates to ensure compatibility with new technologies.
Continuous monitoring to identify and fix faults.
Adaptation to evolving user needs and market trends.
While websites are easier to maintain, web applications require a more hands-on approach. Regular maintenance ensures that your platform remains reliable, secure, and capable of meeting user expectations.
Tools for Building Web Apps and Websites in 2025

Choosing the right tools for building your website or web app can make a significant difference in your project's success. In 2025, advancements in technology have made it easier than ever to create platforms that are both functional and scalable. Below, you'll find some of the most popular tools for building websites and web apps, along with their key features.
Website Tools
WordPress
WordPress remains one of the most widely used content management systems (CMS) in 2025. It powers over 40% of all websites globally, thanks to its flexibility and extensive plugin ecosystem. You can use WordPress to create anything from a personal blog to a full-fledged e-commerce site. Its user-friendly interface and customizable themes make it accessible even if you have no coding experience.
Fun Fact: The global CMS market is expected to surpass $54 billion by the end of 2025, highlighting the growing demand for platforms like WordPress.
Wix
Wix is a drag-and-drop website builder that simplifies the process of creating visually appealing websites. It offers hundreds of templates tailored to various industries, allowing you to design a professional-looking site in minutes. Wix also includes built-in SEO tools to help your website rank higher on search engines. This platform is ideal for small businesses and individuals who want a quick and easy way to establish an online presence.
Squarespace
Squarespace is known for its sleek, modern templates and robust design capabilities. It caters to creatives, such as photographers and artists, who want to showcase their portfolios. Squarespace also provides integrated e-commerce features, making it a great choice for small online stores. Its intuitive interface ensures that you can build a stunning website without needing technical expertise.
Company | Result |
|---|---|
Chacka Marketing | |
Software One | 3x ROI from Marketing Analytics |
Web App Tools
Momen
Momen is a full-stack no-code platform that allows you to build web apps from start to finish in a single browser-based environment. Momen isn’t just for MVPs—it’s a complete toolkit for building real, interactive web apps from scratch. Whether you’re starting with a simple idea or scaling up a complex product, Momen gives you full control, without needing to write code.
What makes Momen a great web app builder?
All-in-one – Frontend, backend, database, and logic in one place.
Customizable – Build exactly what you need, not just templates.
Interactive – Create apps that users can click, input, and use.
AI-ready – Easily add smart features like AI agents or chat.
No-code simplicity – Build visually with drag-and-drop tools.
From quiz makers to planners to mini-marketplaces, you can bring your ideas to life—no tech background required.
Pro Tip: Momen is perfect when you want more than a prototype. You can fully customize your app and grow it over time—no rebuilds needed.
Lovable
Lovable focuses on simplifying the development of user-friendly web apps. It offers pre-built templates and workflows that reduce the time needed to launch your project. This tool is particularly useful for startups and small businesses looking to create apps with minimal resources. Lovable also emphasizes mobile-first design, ensuring your app performs well across all devices.
Bubble
Bubble is another no-code platform that empowers you to create complex web apps without programming knowledge. It provides a visual editor where you can design your app's interface and define workflows. Bubble is highly versatile, making it suitable for building anything from e-commerce platforms to social media applications. Its scalability ensures that your app can grow alongside your business.
Platform | |
|---|---|
Amazon | 37.8 |
Flipkart | 29.5 |
Amazon (India) | 22.8 |
The rise of no-code and low-code tools like Momen, Lovable, and Bubble reflects a broader trend in web development. By 2025, 70% of new applications are expected to use these technologies, making them essential for businesses aiming to stay competitive.
Which Should You Choose in 2025?
Decision-Making Factors
User Goals (e.g., informational vs interactive)
Your goals play a crucial role in deciding between a website and a web app. If your primary objective is to share information, such as company details or blog posts, a website is the ideal choice. Websites are straightforward and focus on delivering content efficiently. However, if you aim to provide an interactive experience, such as enabling users to shop, collaborate, or customize their experience, a web app is better suited. Users increasingly expect personalized and dynamic platforms that adapt to their needs. Custom web apps excel in offering tailored solutions, seamless integration with existing systems, and the flexibility to adapt to market changes.
Budget and Resources
Your budget and available resources significantly influence your decision. Websites are generally more affordable to build and maintain. Tools like WordPress and Wix allow you to create professional websites without extensive technical expertise. On the other hand, web apps require a larger investment due to their complexity. Development costs include research, design, coding, and ongoing maintenance. However, the return on investment can be substantial. Custom web apps provide scalability, enhanced security, and unique features that can give your business a competitive edge.
Technical Requirements
Consider the technical requirements of your project. Websites typically require minimal backend development and are easier to deploy. They are ideal for businesses with limited technical resources. In contrast, web apps demand robust backend systems to support their interactive features. They often integrate with other software and handle large amounts of data. Metrics like error rates, time-to-market, and digital adoption rates can help you evaluate whether your technical infrastructure can support a web app.
Comparison Checklist
When to Choose a Website
You need a platform to share information or showcase content.
Your budget is limited, and you prefer a cost-effective solution.
You want a simple, easy-to-maintain platform.
Your audience does not require interactive features.
When to Choose a Web App
You aim to provide an interactive experience for your users.
Your business requires tailored solutions to meet specific goals.
Scalability and flexibility are essential for your platform.
You need to integrate with existing systems or manage large datasets.
Enhanced security and unique features are critical for your success.
Tip: Nearly half of all companies prioritize improving customer experience and satisfaction when adopting digital solutions. Metrics like Customer Satisfaction (CSAT) and Net Promoter Score (NPS) can help you measure the success of your chosen platform.
By evaluating these factors, you can make an informed decision that aligns with your goals, budget, and technical capabilities.
Websites and web apps serve distinct purposes. Websites primarily deliver information, while web apps focus on interactivity and functionality. Choosing between the two depends on your goals, resources, and technical needs.
Attribute | Web App | Website |
|---|---|---|
Varies | Mostly informational | |
Components | Interactive features | Static or dynamic content |
Accessibility | Often requires authentication | Often allows unregistered users |
Development | Complex | Simpler |
Costs | Generally higher | Generally lower |
Evaluate your requirements carefully. A clear understanding of your objectives will help you decide whether a website or a web app aligns better with your vision.
FAQ
What is the main difference between a website and a web app?
Websites deliver information, while web apps focus on interactivity. Websites are static or dynamic, but web apps allow users to perform tasks like shopping or editing documents. Your choice depends on your goals and user needs.
Can you turn a website into a web app?
Yes, you can. Developers often add interactive features, such as user accounts or real-time updates, to transform a website into a web app. Tools like Momen or Bubble simplify this process.
Do web apps work offline?
Some web apps, like Progressive Web Apps (PWAs), work offline. They store data locally and sync it when you reconnect to the internet. This feature enhances usability and user experience.
Are web apps more expensive to build than websites?
Yes, web apps usually cost more. They require advanced development for interactivity and backend systems. Websites, on the other hand, are simpler and more affordable to create and maintain.
Which is better for SEO: a website or a web app?
Websites generally perform better for SEO. Search engines easily index static content. Web apps, with dynamic content, may need additional optimization to rank well in search results.
Do you need coding skills to build a web app or website?
No, you don’t. No-code platforms like Momen, Wix, and Bubble let you create web apps or websites without coding. These tools offer drag-and-drop interfaces and pre-built templates.
How do you decide between a website and a web app?
Consider your goals. Choose a website if you need to share information. Opt for a web app if you want to provide interactive features like user accounts, real-time updates, or task management.
Are web apps secure?
Web apps can be secure if you implement proper measures. Use encryption, regular updates, and secure authentication methods to protect user data. Always prioritize security during development and maintenance.
See Also
Understanding Web Applications: Key Differences From Websites
Top 30 Innovative Web App Concepts for 2025 Startups
Top No-Code Platforms for Aspiring Web App Creators in 2025
10 Excellent Alternatives to Bubble for Varied App Requirements

