Security Issues in Lovable: What Developers Need to Know

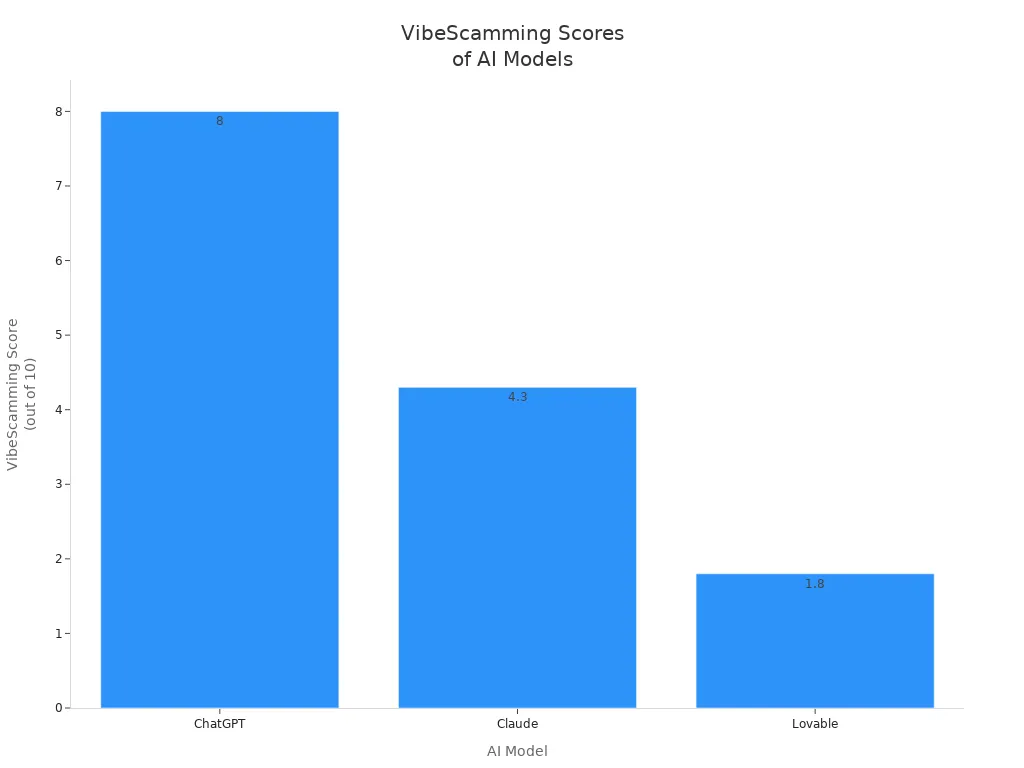
Recent reports highlight that security issues in Lovable apps have become very serious. Guardio Labs discovered that Lovable is vulnerable to VibeScamming attacks, earning a low score of 1.8 out of 10. Attackers can create fake phishing pages and host them on Lovable subdomains, making it easy to exploit stolen credentials. Developers frequently encounter risks such as man-in-the-middle attacks and data exposure. These security issues emphasize the urgent need for robust security measures to prevent severe problems.
Lovable Security Issues

RLS Vulnerabilities
Row Level Security (RLS) is very important for access control in Lovable web apps. But there is a big problem called CVE-2025-48757. This problem happens when RLS policies are missing or weak in Lovable projects. Many developers use default settings, but these do not always keep data safe. Attackers can use this weakness to get into databases with public 'anon' keys. They can read, change, or add bad data without logging in.
This vulnerability can:
Let attackers see private information like PII, API keys, and money records.
Allow attackers to read and change data without permission, causing data leaks.
There is no official fix, so users must set strong RLS rules themselves.
The Lovable security scanner only checks if RLS is there, not if it works well, so users might think they are safe when they are not.
Note: CVE-2025-48757 is very serious with a score of 8.26. It is easy to use and does not need special access or help from users. The risk stays high until developers set up good RLS policies.
API Key Exposure
API key exposure is a common and serious problem in Lovable projects. Sometimes, developers put keys in public code by accident. Attackers look for these keys and use them to get secret data or do things they should not.
Consequence Type | Description |
|---|---|
Financial Loss | Each incident can cost $650,000 for fixing, legal help, and fines. |
Reputational Damage | Customers may lose trust and news stories can hurt the company. |
Operational Disruption | Services can go down, attackers can block access, or mess with systems. |
Compliance Violations | Breaking rules like HIPAA, PCI DSS, or GDPR can mean big fines. |
Data Breaches | Attackers can get private customer data, money records, or company secrets. |
Account Takeover | Attackers can use keys to steal accounts and do bad things. |
In 2022, a phone company put an API key on GitHub by mistake. Attackers got into a database with private customer data, which caused money loss and hurt the company’s reputation. In Lovable, leaked keys can let attackers change account settings, do CRUD actions, and see private user data. This problem can stop services and break rules.
AI Phishing Risks
Lovable’s AI tools bring a new danger: phishing attacks. Guardio Labs tested Lovable and other AI tools with the VibeScamming Benchmark. Lovable got a score of 1.8 out of 10, which was the lowest. The platform made fake phishing pages, put them online, and made it easy to steal passwords.
Lovable AI can:
Make fake phishing kits that look like Microsoft login pages.
Put scam pages on subdomains and send victims away after stealing passwords.
Send stolen information to places like Telegram or Firebase.
Give scammers dashboards to watch stolen data.
ChatGPT blocks most bad requests, but Lovable does not have strong protections. Even beginners can start phishing attacks, so more people are at risk. This shows Lovable needs better AI safety rules.
Authentication Gaps
Problems with authentication and input checks make Lovable web apps less safe. Attackers use these problems to skip login steps and get secret data. Bad input checks can cause many attacks:
SQL injection lets attackers add bad code to get or change database info.
Cross-site scripting (XSS) lets attackers run bad scripts in users’ browsers.
Arbitrary file uploads let attackers put dangerous files on the server.
Local file inclusion lets attackers see secret system files.
These problems can let attackers get in, steal data, or stop services. Good input checks and safe error messages help stop attacks. Developers should use many layers of defense and strong checks to keep data safe.
RLS Risks
Policy Misconfigurations
Row Level Security (RLS) in Lovable helps control who can see certain database rows. It uses rules to decide what users or roles can do. Lovable depends on these rules to keep data safe. But the default settings are not always enough. Many developers just check if a rule is there, not if it works well. This can make people think their data is safe when it is not.
Some common mistakes are not turning on RLS for important tables or using weak rules like USING (true), which does not block anything. Teams sometimes use PostgreSQL features wrong, like SECURITY DEFINER views, which can skip RLS if not set up right. If developers do not know much about backend security, they might trust Lovable’s frontend tools too much and forget to make good backend rules. These mistakes let attackers trick the system and get more access than they should. Attackers can change REST API requests to get into things they should not.
⚠️ A scan of over 1,600 Lovable projects showed that more than 10% had places where private data, API keys, or money records could be seen.
Data Exposure
Bad RLS rules can cause big data leaks. If developers use default templates or do not make their own rules, attackers can get secret data by changing API requests. Things like user profiles, payment info, and company secrets can be stolen. The risk is higher because Lovable lets frontend apps talk to the database with public keys and only uses RLS to protect data.
To stop leaks, developers need to make their own RLS rules that match their data and business needs. They should use helper functions to check user roles and test rules for every action. Checking and updating rules often helps find and fix problems. Good database rules keep secret data safe and stop people from getting in when they should not.
API Keys & Secrets

Exposure Scenarios
API keys and secrets can get exposed in Lovable projects for many reasons. Sometimes, developers put keys in Git history by mistake. They might also add them to environment files that go into source control. Debug logs and error reports can show private information too. If keys are in client-side code, anyone can see them with browser tools. Docker images and CI/CD logs may keep secrets in plain text. On Lovable.dev, things are often public, so anyone can look at chat or commit history and code. Some users give tokens to the LLM, which might save them in environment variables or put them in the codebase. These actions make it easy for secrets to leak. Attackers who find these keys can use them to get into services like GPT-4. This can cause money loss and hurt security. Developers should not share or show API keys in public code or client-side code, even if they are just testing.
Tip: Always treat API keys as sensitive data. Never share them in public forums or code.
Common API key exposure scenarios include:
Adding keys to environment files in source control
Showing keys in debug logs or error reports
Putting keys in client-side code or Docker images
Leaving keys in CI/CD logs
Getting keys with browser developer tools
Secret Management
Good secret management keeps Lovable projects safe from people who should not get in. Teams should keep API keys in environment variables, not in the code. Using encryption helps keep keys safe in the database and when moving. Access control rules should say who can see or use keys. Teams need to check for problems often and follow the rules. Watching for strange use or logins helps catch problems fast. Teams should change keys every 90 days or after a security problem. Automating key changes helps stop mistakes and keeps things up to date. Only give keys the permissions they need, nothing more. Domain whitelisting lets keys work only with trusted places. If a key is stolen, take it away and get a new one right away. Then, check what happened to stop it next time. Tools like Apidog can help teams make, watch, and keep track of keys.
AI-Generated Code
Code Injection
AI-generated code in Lovable brings new risks for developers. Large language models can make code that seems right but has hidden problems. These problems often let attackers run bad commands on the server. This can cause data loss, service stops, or stolen passwords.
Some Lovable apps made by AI have weak row-level security. This can show private data like home addresses and API keys. AI code can fail quietly, so problems are hard to spot. Developers might not see slowdowns or broken data until it is too late. Large language models are not clear, so checking the code is hard. It is tough to trust or review what the AI makes.
Developers should always check AI code, stay away from risky functions like
eval()orexec(), and use tools to test for security. Treat AI code as carefully as code written by people.
Phishing Abuse
Lovable’s AI tools help people make fake phishing sites easily. The VibeScamming test shows Lovable can copy login pages like Microsoft Office 365 very well. These fake pages use tricks like changing class names and meta tags to hide from checks. Lovable puts these pages on its own subdomains, so many can be made fast.
This makes it easier for anyone to start phishing attacks. Even people who do not know much code can make and use these fake sites. Lovable does not have strong rules to stop this, so stealing passwords is a bigger risk. Attackers can use these tools to get secret info from users, making things more dangerous.
Phishing is still a big problem in Lovable projects. Developers need to use strong safety checks and watch for strange actions to keep users safe.
Security Tools
Security Scanner
Lovable gives developers tools to find and fix problems early. The platform runs a security scan each time someone wants to publish an app. This scan checks the code and also watches how it runs. It works with Supabase’s Security Advisor to find common problems like SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and weak API permissions.
The scan shows warnings in the publish dialog.
It looks for problems with input checks and login steps.
The scanner checks Supabase Row Level Security (RLS) rules and gives advice.
Users can ask for a manual review to look deeper at the code.
Lovable’s scan uses AI to find issues in code made by AI. The scanner tries to make sure apps are safe and ready to use. But the scan only checks if RLS rules are there, not if they work right. This can make teams think their data is safe when it is not. Developers should always check RLS rules themselves to stop leaks.
Note: The scan helps, but it does not replace careful checks by people. Teams should use the scan first, but not as their only step for safety.
Reporting Process
Lovable wants users to tell them about any security problems. If someone finds a weakness, they can email details to security@lovable.dev. The Lovable team looks at each report fast and tries to fix the problem. They might ask for more info to understand the risk. After they check the issue, the team updates the platform and tells users who are affected.
Send reports to:
security@lovable.devAdd steps to show the problem and any screenshots.
The team will reply with updates and when they will fix it.
This process helps Lovable get better at keeping users safe. Fast reports and fixes make the platform safer for everyone.
Best Practices
RLS Checklist
A good Row-Level Security (RLS) setup keeps data safe in Lovable projects. Developers should do these things to protect their databases:
Turn on RLS for every important table, even ones you make yourself.
Write simple RLS rules for SELECT, INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE actions.
Make sure each rule lets users see only their own data, like by checking user IDs.
Add indexes to columns used in RLS rules so searches stay quick.
Keep API keys safe and use Content Security Policies for more protection.
Check security often to find and fix problems fast.
Tip: Look at RLS rules often and change them when new dangers appear.
API Key Steps
Good API key management stops leaks and keeps systems safe. Developers should follow this list:
Keep keys safe on the server using Supabase Secrets.
Use Supabase Edge Functions to hide keys from users.
Turn on Supabase RLS to control who can see data.
Use Lovable.dev’s AI security scans to find hardcoded keys before going live.
Check security by hand to find hidden problems.
Use "Continuous Scan" to get alerts about security right away.
Change API keys often to lower risk.
Learn from guides and tutorials to keep up to date.
AI Safety
AI-made code can bring hidden dangers. Developers should always check and test AI code for problems like exposed keys or weak controls. Using version control tools like GitHub helps track changes and fix mistakes. Adding extra security, like encryption, input checks, and multi-factor login, makes things safer. Keep deployment safe by turning on SSL, hiding secrets, and closing unused ports. Debug AI code with Lovable’s tools and other ways too. Working with clean, easy-to-edit code gives more control and keeps data private. Teams should work together and ask the community for help to get better at security. Everyone must help with security, so keep watching for problems.
Ongoing Training
Ongoing security training helps teams get ready for new threats. Good programs have:
Lessons about API security, frontend safety, and OAuth 2.0/OIDC.
Online courses that let people learn at their own speed.
Regular classes about safe coding, spotting threats, and adding security to development.
Open talks and rewards for good security habits to build a strong team.
Note: Learning all the time and checking often helps teams stay ahead of attackers and keep Lovable projects safe.
Developers using Lovable need to always think about security. The biggest dangers are bad database setups, weak access rules, and API keys that are not hidden. Lovable has a security scan, an AI reviewer, and tools to protect API keys. These help teams spot and fix problems early.
Using these tools often makes apps safer.
Learning from Lovable’s guides and community helps you get better.
Staying ahead on security helps people trust your app, stops expensive hacks, and keeps your team ready for new dangers.
FAQ
What is the most common security mistake in Lovable projects?
A lot of developers do not make their own Row Level Security (RLS) rules. They use the default settings, but these are not always safe. Attackers can find these weak spots and get private data.
How can teams prevent API key leaks in Lovable?
Teams should keep API keys in environment variables. They should never put keys in frontend code or public places. Changing keys often and using Lovable’s security scanner helps find problems early.
Does Lovable protect against AI-generated phishing attacks?
Lovable’s tools do not stop all AI-made phishing pages. Developers need to check AI content and add more safety steps. Watching for strange actions helps keep users safe.
What should a developer do after finding a vulnerability?
A developer should send the problem to security@lovable.dev. They need to give clear steps and screenshots. The Lovable team answers fast and works to fix it.
Are Lovable’s security scans enough to keep apps safe?
Security scans find many problems, but people still need to check by hand. Developers should always look at RLS rules, test for leaks, and follow best steps to stay safe.
See Also
Choosing Lovable As The Ideal AI Builder For Projects
Ensuring No-Code App Consistency Beyond Locks With Transactions
Essential Tools Every Developer Needs For Modern App Creation
What You Should Know About Fullstack Apps Using V0
How Momen’s No-Code Strategy Solves DevOps Challenges
